Food waste prevention in Europe can generate major footprint savings
New calculations show that the European countries have great potential for reducing the demand for global food resources and the associated GHG footprint. Researchers have estimated the climate footprint savings that may be obtained from reducing food loss and waste along Europe’s food supply chain by 50 % by 2030.
New research shows that European food consumption draws unnecessarily excessively on global resources, which is why researchers are calling for political action. Many of the foods that are consumed in Europe are produced in countries outside Europe. Food loss – and waste later in the chain, (see box on waste terms) – occurs along the food supply chain, from the primary agricultural sector in Europe or rest of the world, until it feeds mouths in Europe.
Waste Terminology
In an international context, “food loss” occurs from the primary agricultural sector to the food processing industry and the wholesale sector, while from the retail sector towards the service industry and households, we refer to “food waste”.
food loss
“Halving Europe’s food loss and waste, together with a redistribution of global food resources, could solve the challenges of food shortages in the world,” says Marianne Thomsen, research leader and professor of sustainable food systems at the Department of Food Science at the University of Copenhagen (UCPH FOOD).
“Halving Europe’s food loss and waste, together with a redistribution of global food resources, could solve the challenges of food shortages in the world,” explains Marianne Thomsen, research leader and professor of sustainable food systems at the Department of Food Science at the University of Copenhagen (UCPH FOOD).
This is why countries should invest in solutions to reduce food loss and waste at all stages of the food supply chain, believes Marianne Thomsen.
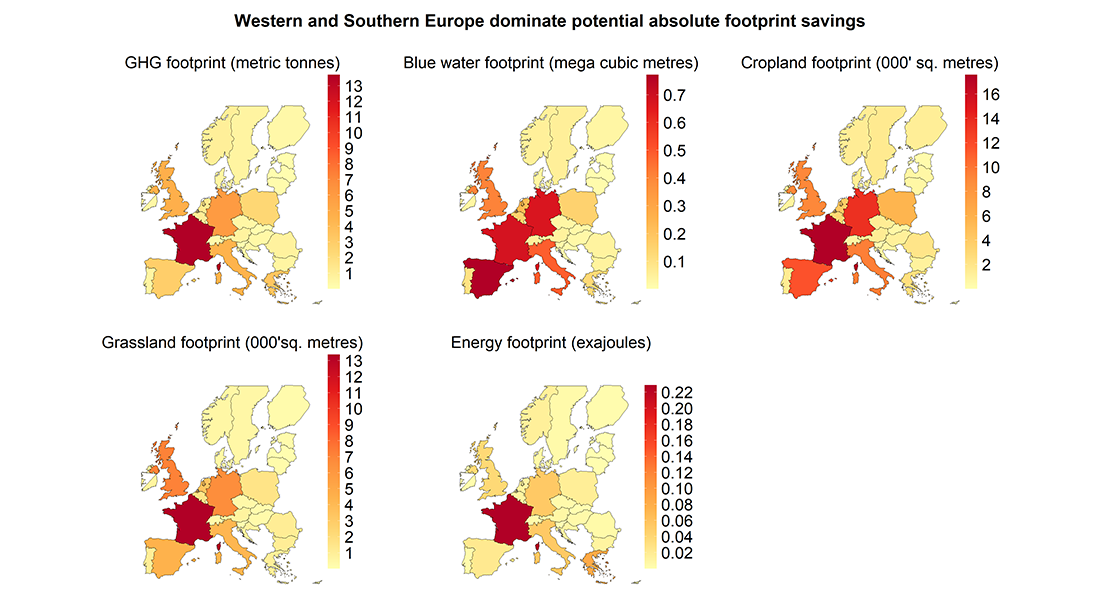
Figure 1. Western and Southern Europe in particular dominate potential absolute footprint savings (“absolute” as opposed to per capita footprint savings, as shown in figure 2). GHG = greenhouse gases, Blue water footprint = water consumption, Cropland = agricultural areas, Grassland = grazing areas and Energy = energy consumption. Illustration: Albert Osei-Owusu
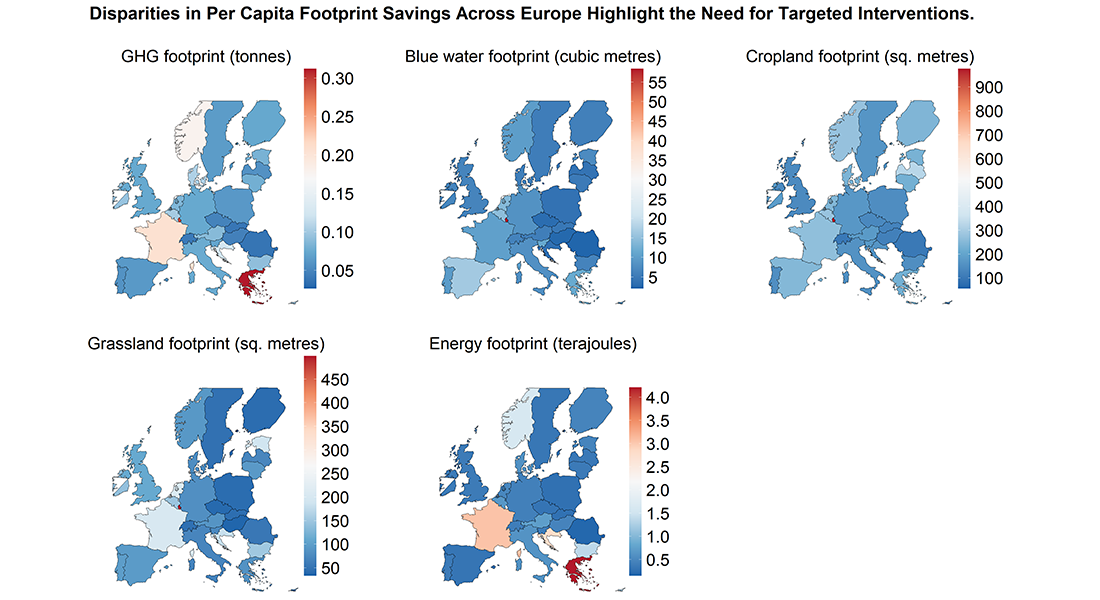
Figure 2. The illustration shows that there is a difference in how much the individual countries in Europe can potentially save in footprint per capita measured by five different footprint indicators: Greenhouse gas emissions (GHG footprint), water consumption (Blue water footprint), agricultural areas (Cropland), grazing areas (Grassland) and energy consumption (Energy). Illustration: Albert Osei-Owusu
Gains from reducing food loss and waste
The researchers’ scenario calculations show what will happen if we halve the food loss and waste along the food supply chains associated with Europe’s food consumption. Halving food loss and waste in Europe’s food supply chains equates to saving 8 % of the greenhouse gas emissions caused by food consumption in Europe, along with an associated saving of 6 % of agricultural areas and 6 % of grazing areas – overall equalling 12 % of agricultural areas – as grazing areas are used for livestock. In addition, there is a saving of 7 % of water consumption, and 14 % of energy embodied in the food production for the citizens of Europe (see also the box with calculations).
The calculations:
The calculations are based on world food production and trade in 2018. By reducing the food loss and waste resulting from European food consumption by 50 %, the following consumption-based footprint savings can be achieved:
- 51 million tonnes CO2 equivalents (8%)
- 106,446 km2 agricultural land use (6 %)
- 55,523 km2 use of grazing land (6 %)
- 4.6 billion m3 water savings (7 %)
- 131 terawatt-hours (0.47 exajoules) energy savings (14 %)
Marianne Thomsen points towards monitoring and reporting of food loss and waste by all actors along the food supply chain as an important policy instrument.

There is a need to invest in reducing food loss and waste associated with European food consumption at all stages of the food supply chain from farm to fork,” says Marianne Thomsen, professor at the Department of Food Science at the University of Copenhagen (UCPH FOOD). Picture: Lene Hundborg Koss
Marianne Thomsen points towards monitoring and reporting of food loss and waste by all actors along the food supply chain as an important policy instrument.
“Such a policy instrument may, supported by other types of policy instruments, be a strong incentive for companies and the rest of society to invest time and money in new technology and collaboration to prevent food loss and waste by closing the loop along the food supply chains within local circular food systems,” she says.
Marianne Thomsen also provides some examples of where food waste can be prevented:
“The companies can collaborate on sustainable innovation in circular symbioses where side streams are utilized for producing upcycled ingredients and products. As another example, the service industry can apply upcycled ingredients produced from surplus food in the wholesale sector, while at the same time nudge costumers to take smaller portions by reducing the plate size,” she explains.
A new angle on Europe’s footprint
National greenhouse gas emission inventories are based on the amount of greenhouse gases emitted by individual countries from the food production that occurs within their own geographical borders. The new calculations apply a consumption-based accounting approach. This includes the climate footprint from locally produced and imported food in European countries, while excluding domestically produced foods exported to other countries. In the scenario calculations, the researchers have assumed that the reduction in food loss and waste occurs through prevention, generating a reduction in food production and supply to satisfy European food consumption.
“Cutting food loss and waste caused by Europe’s food consumption by 50 % requires political intervention, and also that policy interventions are adapted to national circumstances and specific regional and local challenges,” says Marianne Thomsen.
The calculations show that there are large regional differences determining the most effective intervention type. That said, Western Europeans show the greatest potential footprint savings, especially France, Germany, Belgium, and the Netherlands. But also, countries with a lower gross domestic product, such as Greece, Croatia, Bulgaria, and Romania have great potential for food waste prevention. The agricultural sector shows the greatest potential for reducing the climate footprint, while the greatest potential for saving energy is found in the service industry, which includes canteens, hotels, and restaurants.
The scientific article:
The article is published in Environmental Science & Technology.
DOI: 10.1021/acs.est.3c00158
Authors:
Marianne Thomsen, Professor of Sustainability Assessment – Sustainable Food Processing and Production at the Department of Food Science at the University of Copenhagen (UCPH FOOD) (research leader), Green Solutions Center, Fighting food waste Thematic solutions – University of Copenhagen.
Albert Kwame Osei-Owusu, Postdoc at the Department of Sustainability and Planning, Aalborg University.
Quentin D. Read, Statistician at the U.S. Department of Agriculture’s Agricultural Research Service (ARS)
The research study is co-financed by the EU project FOODRUS, which aims to prevent food loss and waste in Europe and identify and implement innovative circular solutions for resilient food systems.
The research study applies multi-regional input-output modelling to estimate the potential footprint savings that result from reducing current FLW levels in Europe by 50%. The baseline, for calculating the impact of food loss and waste prevention, is the world food production and trade in 2018, pre-COVID-19.
Contact
Professor at the Department of Food Science at the University of Copenhagen (UCPH FOOD) Marianne Thomsen, mth@food.ku.dk
or
Communications Officer at UCPH FOOD Lene Hundborg Koss, lene.h.koss@food.ku.dk
