RNA trickery disarms the antiviral CRISPR defenses of bacteria
Bacteria-attacking viruses, known as bacteriophages, use small RNAs to disarm the CRISPR-Cas immune systems of bacteria. This discovery has now been documented by researchers at the University of Copenhagen. The inhibitory RNAs named "Racrs" are a significant breakthrough in efforts to control CRISPR-Cas technologies and improve phage therapy, an alternative to antibiotics.
The microbial world is a battlefield where microscopic organisms constantly fight for resources, survival, and reproduction. Bacteria are targeted by bacteriophages (phages) and other genetic parasites that can only replicate by invading bacteria.
CRISPR-Cas systems are one of the primary defense mechanisms used by bacteria to protect themselves against phages. These systems use small “memorized” pieces of phage DNA to make RNA molecules that guide Cas protein “genetic scissors” to cut up re-invading phages.
Using these CRISPR-Cas scissors as a genome editing tool also led to the 2020 chemistry Nobel Prize, and the use of phages to treat bacterial infections is a 100-year-old alternative to antibiotics, which was mostly forgotten by western medicine, but has reemerged, due to the rising antibiotic resistance crisis.
In a new research article, scientists from the University of Copenhagen, collaborating with colleagues at the University of Otago in New Zealand, identified a countermeasure in this microscopic arms race that could open new doors for medical science – possibly in the form of safer CRISPR-Cas treatments and enhanced phage therapy approaches.
“We characterized a fascinating new strategy employed by phages to switch off the bacterial CRISPR-Cas immune response,” says Rafael Pinilla-Redondo, an assistant professor at the Department of Biology who led the Copenhagen team’s research efforts.
In a previous study, researchers identified sequences resembling parts of the immune memory (the CRISPR repeats) on phage genomes, yet their function had remained a mystery. Now, the Copenhagen and Otago researchers have found that phages can use these small RNAs to disarm the bacteria’s CRISPR-Cas defense mechanisms.
“We find that phages use these small RNAs that mimic part of CRISPR-Cas systems as decoys for the immune system components. This trickery allows the phages to infect bacteria," explains Ph.D. Sarah Camara from the Department of Biology, who is the lead author of the article together with Ph.D. David Mayo-Muñoz from the University of Otago.
The researchers also find that these molecular RNA mimics lead to the assembly of dysfunctional CRISPR-Cas immune complexes, which do not carry all the crucial proteins necessary to clear the phage infection.
“The strategy appears to be widespread, which is of great interest to the scientific community and a significant advancement in the field of CRISPR-Cas," adds Professor Søren J. Sørensen from the Department of Biology, who supervised and is a co-author of the new research article.
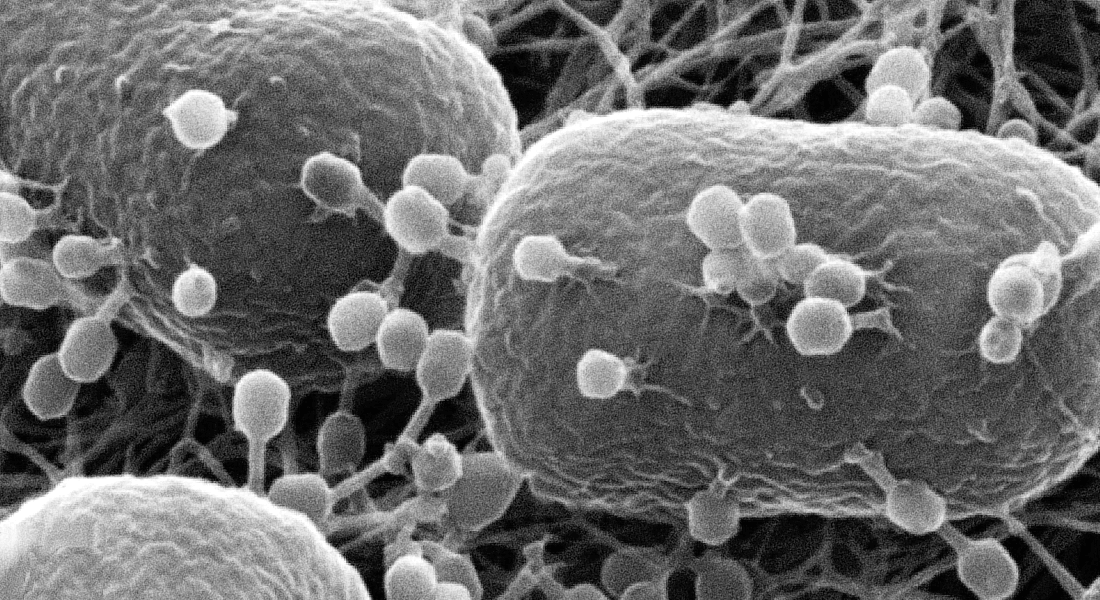
Empowering an alternative to antibiotics
The discovery of Racrs could be a breakthrough for phage therapy, an alternative way of combatting pathogenic bacteria making phage therapy a better way to treat infections instead of antibiotics.
Today, antibiotic resistance has become one of the most significant threats to global public health, with dangerous infections caused by so-called superbugs killing more than one million people worldwide every year. This number is expected to increase tenfold by 2050.
Experts say the era of antibiotics is drawing to a close. Because of this, phage therapy is making a comeback. The discovery of Racrs could end up improving such therapies in the future.
“Alternatives to antibiotics need to be found and it is becoming evident that phage therapy can be effective while also being highly specific,” explains Professor Søren Sørensen.
"Whereas penicillin has a broad impact and kills a whole range of bacteria, including our gut microbiota – which is far from ideal – phages are much more specific in terms of the bacteria that they target," adds Søren Sørensen.
However, a key challenge for phage therapy is that bacteria can develop immunity to phages using CRISPR-Cas systems. This is where Racrs come into play. Along with anti-CRISPR proteins previously discovered, the hope is that scientists can design phages carrying these CRISPR-Cas inhibiting Racrs, and thereby block the immune defenses of bacteria.
Safer CRISPR Treatments
Another promising perspective for Racrs is in controlling the activity of CRISPR-Cas biotechnologies, thereby making them safer and more precise.
Another promising perspective for Racrs is in controlling the activity of CRISPR-Cas biotechnologies, thereby making them safer and more precise.
Fatcs: How Racrs work
Bacteria use CRISPR-Cas as an immune defense against phages and other genetic parasites. Small pieces of foreign DNA are stored as “mugshots” in the bacterium’s “CRISPR memory”. This memory is then transformed into RNAs that guide protein scissors (Cas) to matching sequences in genetic intruders and cut them apart.
Together, the components form what are known as CRISPR-Cas effector complexes, which can both locate and destroy foreign genetic parasites, such as phages.
Racrs are RNA fragments from phages that act as RNA-guide decoys. By mimicking parts of RNA-guides, they interact with Cas proteins. As a result, they form complexes that lack critical components and are thereby dysfunctional.
These rapidly evolving treatments can be used to make direct changes to DNA and are becoming more popular in genetic engineering.
However, these technologies remain challenging to control once they have been administered to cells. Consequently, there is a strong demand for ways to control the CRISPR-Cas toolbox.
These rapidly evolving treatments can be used to make direct changes to DNA and are becoming more popular in genetic engineering. However, these technologies remain challenging to control once they have been administered to cells. Consequently, there is a strong demand for ways to control the CRISPR-Cas toolbox.
“Racrs could potentially be used to create more specific and controlled treatments because anti-CRISPRs offer us the opportunity to control the activity of CRISPR-Cas gene scissors,” says Assistant Professor Rafael Pinilla-Redondo.
Proteins in a Haystack and Indexed RNA
The identification of anti-CRISPR proteins a decade ago drew much attention from researchers and prodigious research funding due to biotechnological hopes. But finding anti-CRISPR proteins has proved difficult.
“This is not the case with RNA-based Racrs. Because these anti-CRISPRs mimic parts of the bacterial CRISPR repeats, it simplifies their identification and may offer the potential for their rational design,” explains Rafael Pinilla-Redondo.
Behind the research
The following researchers have contributed to the research study:
Sarah Camara-Wilpert, Jakob Russel, Jonas S. Madsen, Søren J. Sørensen, and Rafael Pinilla-Redondo from the Department of Biology at the University of Copenhagen.
David Mayo-Muñoz, Robert D. Fagerlund, and Peter C. Fineran from Otago University, New Zealand.
Contact
Sarah Camara-Wilpert
Ph.D.
Department of Biology
University of Copenhagen
Rafael Pinilla Redondo
Assistant Professor
Department of Biology
University of Copenhagen
rafael.pinilla@bio.ku.dk
35 32 80 49
Søren Johannes Sørensen
Professor
Department of Biology
University of Copenhagen
sjs@bio.ku.dk
51 82 70 07
Kristian Bjørn-Hansen
Journalist and Press Contact
Faculty of Science
University of Copenhagen
kbh@science.ku.dk
93 51 60 02
