
News about Bacteria
Viser 1 til 24 af 82 dokumenter.


Global change and antibiotic resistance gene dissemination through horizontal gene transfer

Proof of Concept grant to explore innovative research

From Archived Brains to Future Psychiatry: Revealing the role of infection in mental health
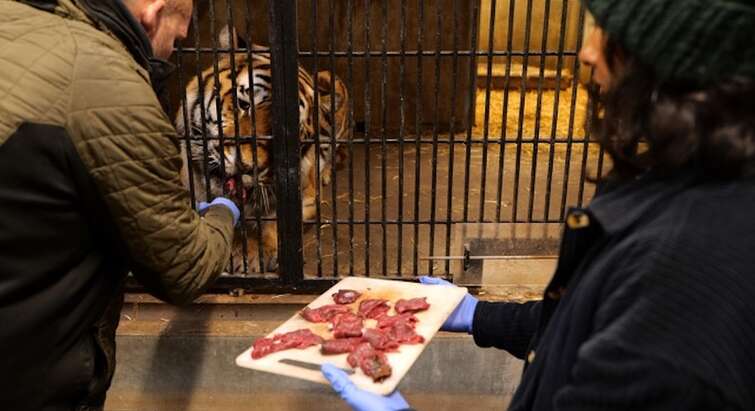

Researchers test “smart-pill” to explore tiger stomach microbiomes

Genetics and gill microbes work together to shape salmon disease resistance

Researchers revive yoghurt made from... ants

Researchers revive yoghurt made from... ants

Stored for 130 years: Bottles reveal evidence of Danish butter production and hygiene practices of the past
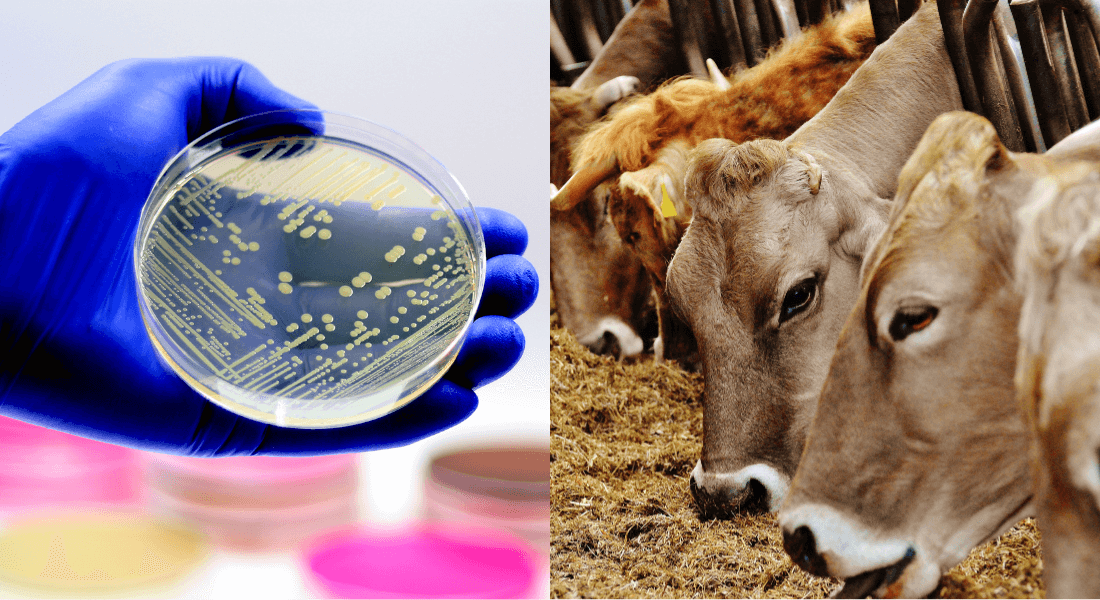

Bacteria from cows show promising results in treating MRSA infections

Dangerous Variant of Salmonella Still Not Eradicated

CLEAR Network workshop Madrid 2025

Bjarne Styrishave, our new professor of drug toxicology

Bacteria Use Ancient War Trick to Outsmart Viruses – and It Could Help Us Fight Superbugs

Aves KL et al. Vaccines 13, 207, 2025
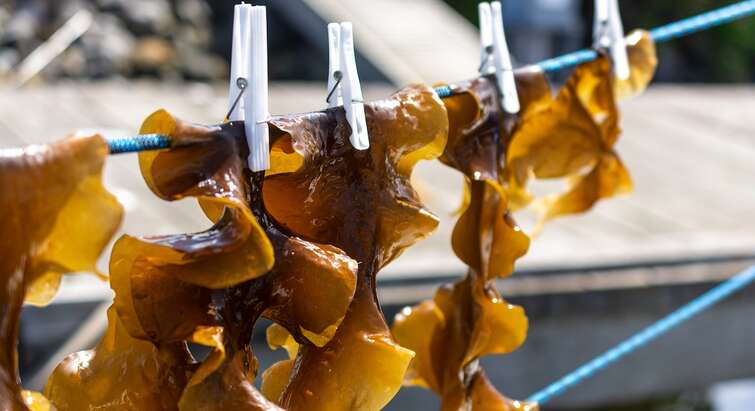

Fermented seaweed found to boost gut health and immunity in Atlantic Salmon

New insights into hologenomics research in wild vertebrates
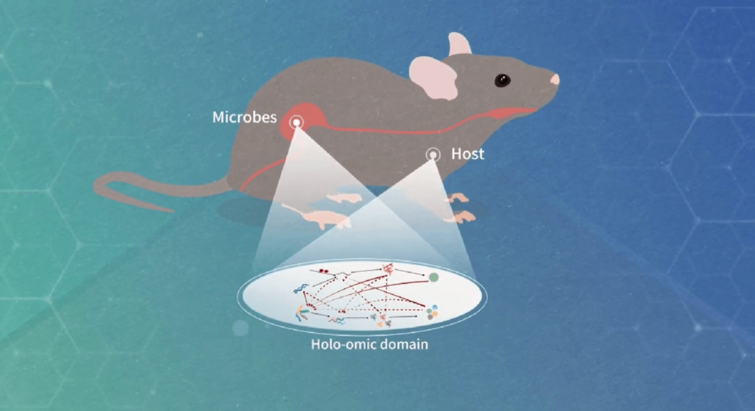
New perspective on the interaction between host organisms and microbes can transform food production and medicine

New perspective on the interaction between host organisms and microbes can transform food production and medicine

Researchers hope to develop novel drugs for gastrointestinal disorders by fermenting feces

Researchers hope to develop novel drugs for gastrointestinal disorders by fermenting feces
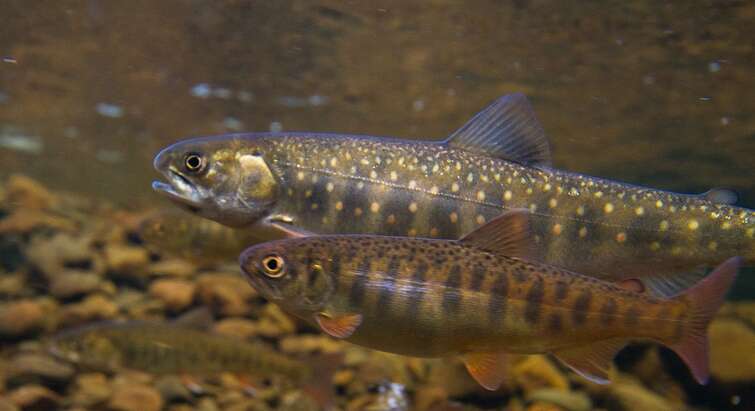

New grant to explore how microbes drive evolution in host organisms
New international network to train researchers in hologenomics

