
News about Health
Viser 73 til 96 af 1447 dokumenter.


Carsten Kirkeby presents HPAI research at Nordic Poultry Conference 2025
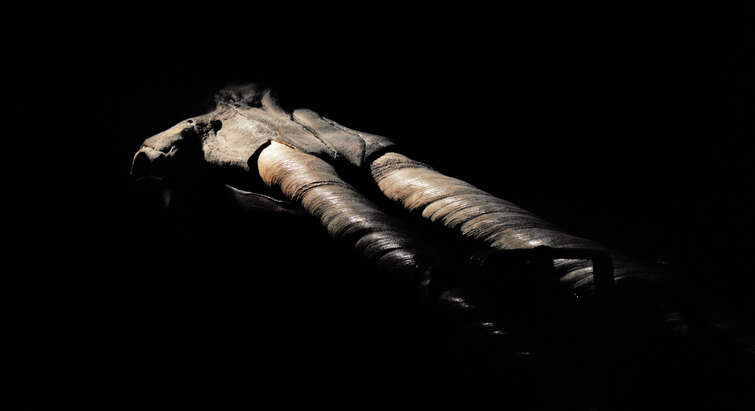
Anomalous two-tusked narwhals show no difference in diet or foraging ecology relative to normal narwhals

Breast cancer treatments can improve both survival chances and income

New Insights into Senataxin’s Role in Transcription

The world’s oldest RNA extracted from woolly mammoth

The world’s oldest RNA extracted from woolly mammoth

Martinez-Vega R et al. BMC Infect Dis 25: 1547, 2025

National Congress of the Italian Society of Microbiology SIM 2025

STAPHGBI2025

Three researchers at SUND are Ascending Investigators

Two Ascending Investigators

Watch: Co-Creation of Mosquito Control Solutions in Zanzibar Hospitals

DGHM–VAAM 2024

Genetics and gill microbes work together to shape salmon disease resistance
Independent Research Fund Denmark funded four new research projects

National Congress of the Italian Society of Microbiology (SIM 2024) Pavia

New Approaches to Combat Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Conference Ascona

Nordic Zebrafish Network meeting 2025

Jessica Preston joins CMP
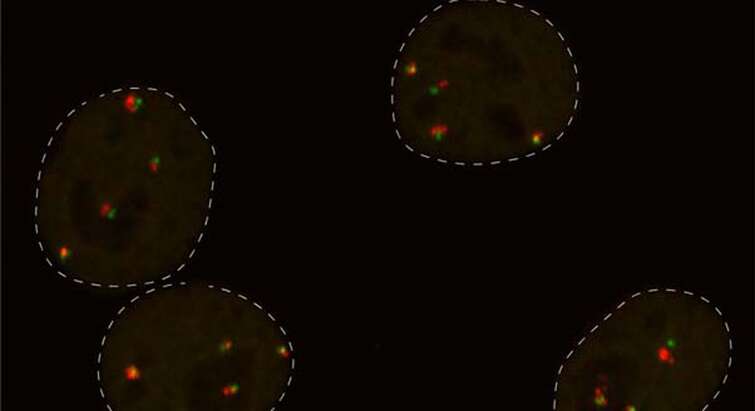
DNA Repair's Hidden Cost: Why 'Fixed' Cells Never Fully Recover

Innovation, Law, and Ethics in International Bioscience – Bill of Health Digital Symposium

Developing advanced mass spectrometry imaging techniques for visualizing peptide drugs

