News about Bacteria
Viser 25 til 48 af 82 dokumenter.
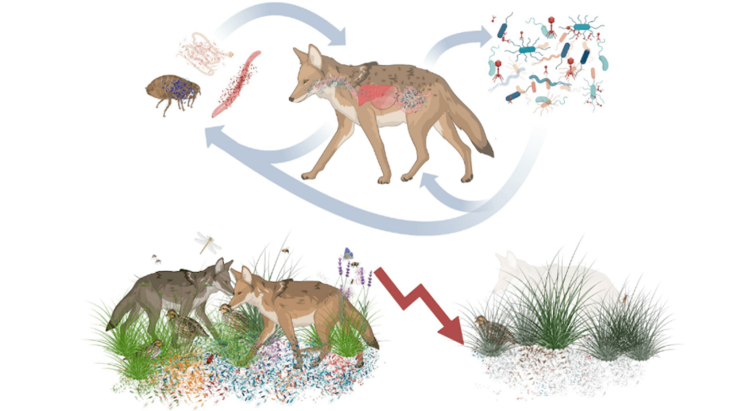
Microorganisms - a key aspect in biodiversity loss

Microorganisms - a key aspect in biodiversity loss

Benjamin Seeks to Improve Gut Health with Bacterial Lysate
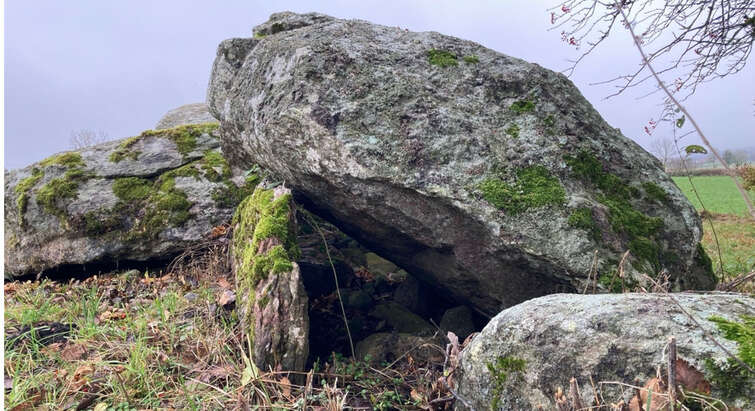

Plague emerges from Stone Age graves
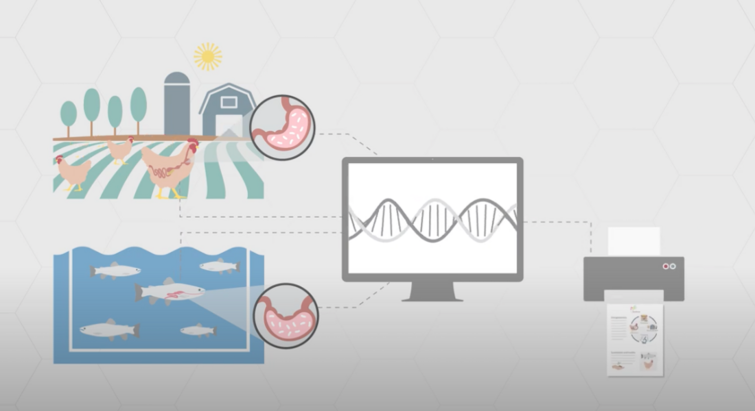
A practical introduction to holo-omics

Exploring the role of root microbiome in plant domestication

Exploring the role of root microbiome in plant domestication

Understanding the interactions between gut microbiome and host epigenetics
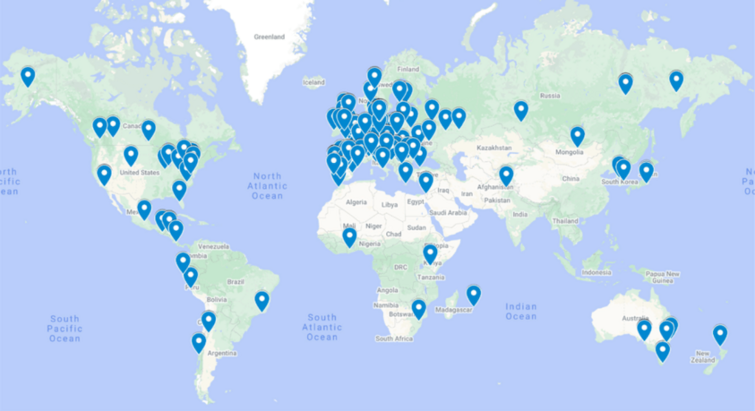
A global collaboration to study animals and their microbiota

Mystery CRISPR unlocked: a new ally against antibiotic resistance?
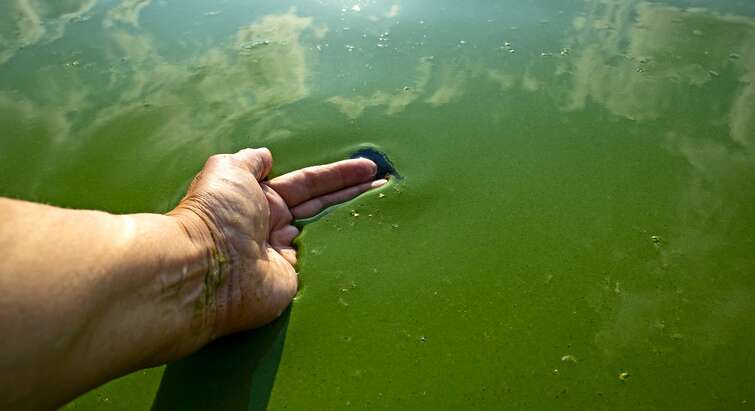

Scientists use blue-green algae as a surrogate mother for "meat-like" proteins

Scientists use blue-green algae as a surrogate mother for "meat-like" proteins
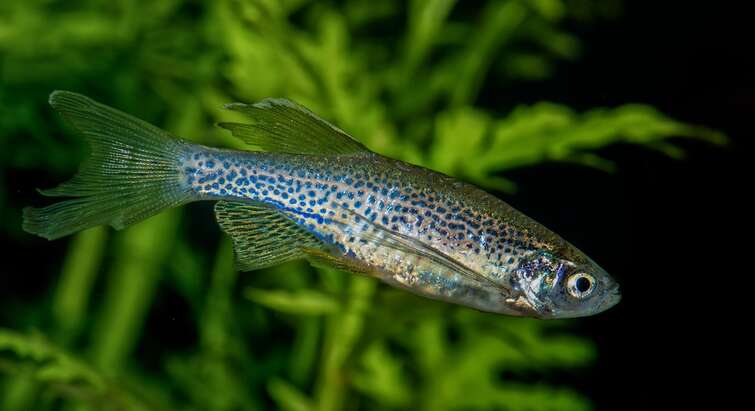

Revolutionary zebrafish model unravels host gene influence on microbiota dynamics
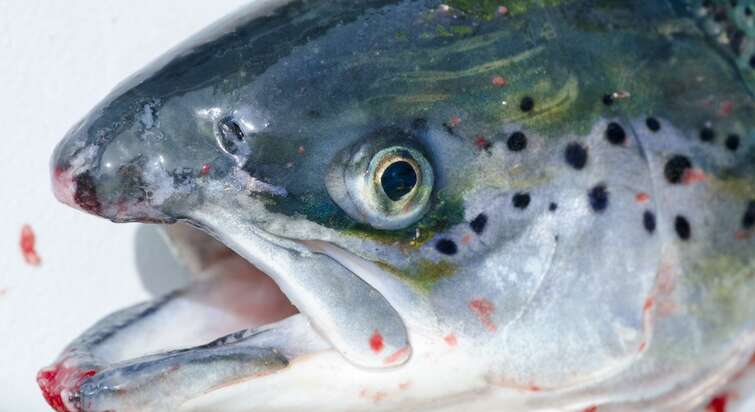

A new hologenomic paradigm for understanding and treating parasite infections

A new hologenomic paradigm for understanding and treating parasite infections
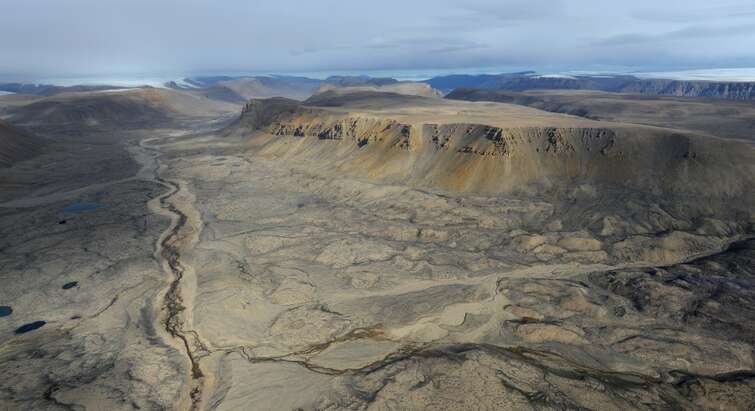

New study reports that Greenland is a methane sink rather than a source

New study unveils link between microbial community succession and secondary metabolites in marine biofilm development
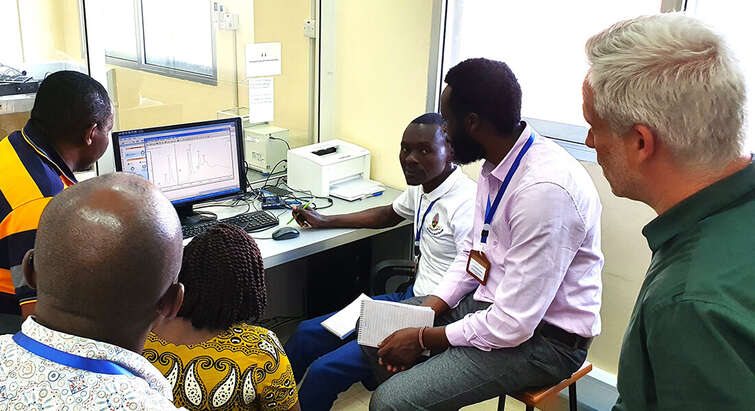

Reducing the use of antibiotics in Kenyan food production

Plant-microbiome interactions for a sustainable future

Uncovering natures lessons in plant-root microbiome co-evolution
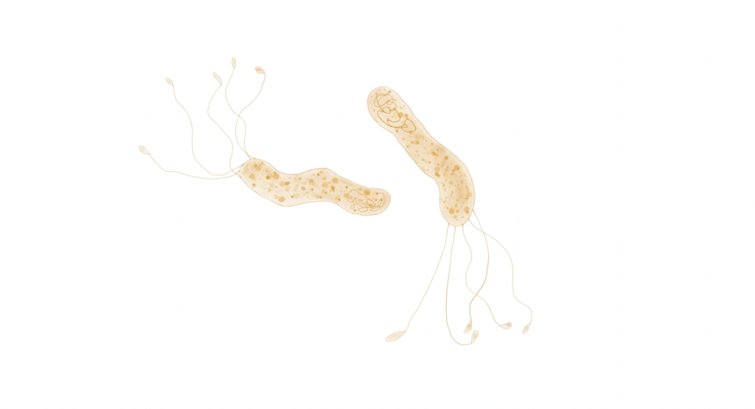
Pioneering project to capture life in the stomach

Bakterier kan hæmme virkning af kræftmedicin

